Accurate Diagnostic Modalities
Family Footcare PC is determined to provide patients with the most accurate diagnostic modalities. Skin biopsies are quick and very useful in the diagnosis of common skin diseases, including but not limited to dermatitis, psoriasis, skin cancers- basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, malignant melanoma, and blistering skin conditions. Even peripheral neuropathy can be diagnosed with a skin biopsy.
Remember, skin cancers of the feet are painless. So if you notice a mole, bump, or patch of abnormal skin on yourself, a friend, or a family member, encourage them to see a doctor and get a biopsy.
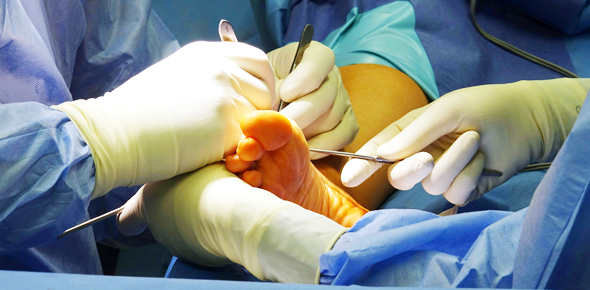
Skin Biopsy
A skin biopsy is a procedure in which a doctor cuts and removes a small sample of skin to have it tested. This sample will have cells that will help the doctor diagnose a number of skin diseases, including skin cancer, infection, dermatitis, and any suspicious moles or skin lesions.
Several types of skin biopsy can be performed in the office setting, including:
- Shave biopsy- A thin layer from the top of the skin lesion is shaved with a razor
- Punch biopsy- An instrument known as a punch is used to remove a circular section through all layers of the skin lesion
- Excisional biopsy- A scalpel is used to remove the entire lesion, lump, or abnormal skin. This is usually only done on smaller lesions
- Incisional biopsy- A scalpel is used to remove a small sample of the large lesion.
To perform a skin biopsy, the skin and lesion are first cleansed, and the area is numbed with local anesthesia injection. The biopsy is then performed using one of the above methods/procedures. In some cases, the biopsy area might be closed with stitches or steri-strips (butterfly stitches) or dressed with a bandage. Post-procedural instructions are given on caring for the biopsy area. The skin sample is then sent to a board-certified dermatopathologist, where skin tissue is examined in greater detail. The biopsy result is usually completed in 1-2 weeks. The doctor will have you back for a follow-up and to go over the results and treatment.
Epidermal Nerve Fiber Density Analysis
Peripheral neuropathy is not uncommon, affecting roughly 15-20 million persons over the age of 40 in the United States. Conditions that may increase the risk of developing the small fiber type/variant of peripheral neuropathy include diabetes, hyperlipidemia, chemotherapy, alcoholism, Sjogren’s syndrome, vasculitis, amyloidosis, lymphoma, HIV, Lyme disease, and idiopathic or no identifiable cause. Affected persons may experience symptoms, which range from burning and tingling to coolness and numbness. Epidermal nerve fiber density analysis is a test that allows your doctor to directly detect the presence of small fiber peripheral neuropathy by evaluating the number and quality of the epidermal nerves in a small sample of skin. With this information, your doctor can both definitively diagnose small fiber neuropathy and assess its degree of severity.
To perform epidermal nerve fiber density analysis, a small biopsy of skin is obtained in the office setting. In most cases, a punch biopsy is performed under local anesthesia. Potential biopsy sites include the lower leg/ankle and dorsum of the foot. The skin sample is then sent to Bako Lab, where the analysis is performed. The test is usually completed in 5-7 business days.